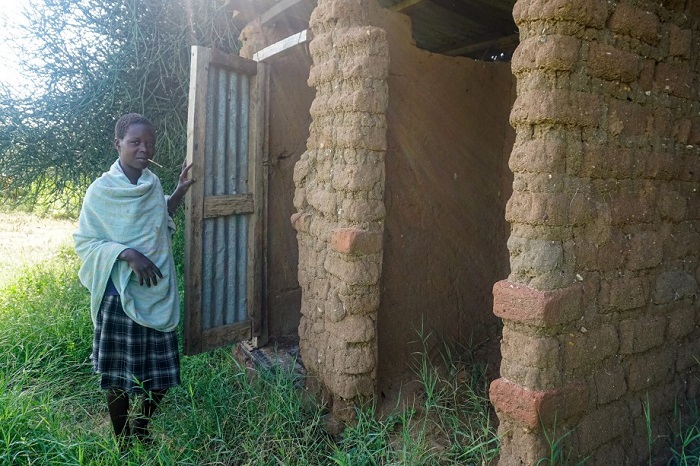
Open defecation is a serious issue that affects the health and well-being of people across the world. In Uganda, open defecation is a significant problem with approximately 14 million of the people engaging in the practice.
Open defecation has a significant impact on water safety, health, and associated factors. This essay will explore the burden of open defecation in Uganda, the associations with water safety, the impact on health, and the associated factors.
Additionally, the essay will discuss what can be done in terms of partnerships between the ministry and NGOs to address the issue. The majority of people who engage in open defecation are in rural areas, with 80% of the rural population practising the behavior. The practice is prevalent among households without toilets or latrines, with many households lacking the means to build or maintain these facilities.
Open defecation has a significant impact on water safety, particularly in Uganda. The practice leads to the contamination of water sources, including lakes, rivers, and streams. The contamination of water sources by human waste can lead to the transmission of diseases, including cholera, typhoid fever, and hepatitis A.
In addition, the contamination of water sources can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites, which can cause illness and death. The contamination of water sources by human waste is a significant problem in Uganda, particularly in rural areas, where the majority of people rely on these sources for drinking, cooking, and washing.
The impact of open defecation on health is significant. In Uganda, the practice is associated with the transmission of diseases, including cholera, typhoid fever, and hepatitis A. These diseases can cause severe illness and, in some cases, death. In addition, open defecation can lead to the spread of other diseases, including diarrhea, which is a leading cause of death among children under five in Uganda. The lack of access to safe sanitation facilities is a significant contributor to the high rates of morbidity and mortality in Uganda.
Several factors contribute to the prevalence of open defecation in Uganda. The lack of access to safe and affordable sanitation facilities is a significant factor. Many households in rural areas lack the means to build or maintain toilets or latrines, leading to the practice of open defecation.
In addition, cultural beliefs and practices also contribute to the prevalence of open defecation. In some cultures, it is considered acceptable to defecate in the open, and changing these beliefs and practices can be challenging. Lack of education on the importance of proper sanitation and hygiene practices is another factor that contributes to the prevalence of open defecation in Uganda.
Addressing the problem of open defecation in Uganda requires collaboration between the ministry and NGOs. The ministry can provide the necessary regulatory framework and policy guidance to address the problem, while NGOs can provide technical expertise and support to implement solutions.
Partnership between the ministry and NGOs can take many forms, including the provision of funding, technical assistance, and capacity building. Additionally, partnerships can help to raise awareness and change cultural beliefs and practices around sanitation and hygiene.
If you would like your article/opinion to be published on Uganda’s most authoritative news platform, send your submission on: [email protected]. You can also follow DailyExpress on WhatsApp and on Twitter (X) for realtime updates.



