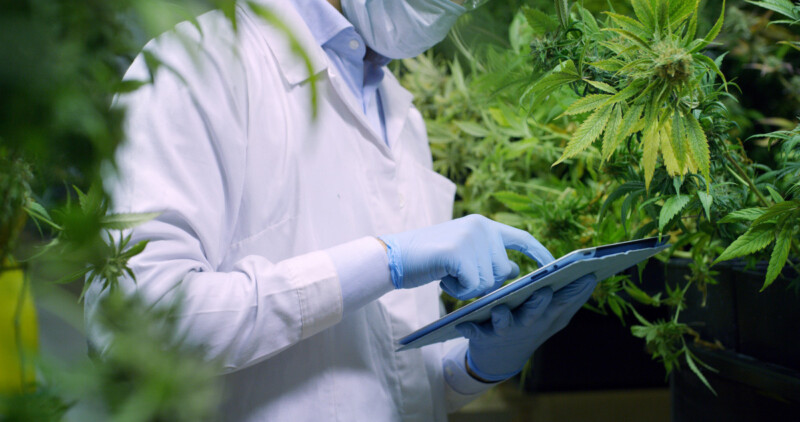
As numerous countries world-over are moving a step further to legalize the growth and medical use of cannabis, Uganda is lagging behind its legalization despite a study proving that the lucrative marijuana plant is less addictive (and safer) than alcohol and cigarette, especially for medicinal purposes.
Uganda is still among the countries that have not yet legalized cannabis growing despite its troubled economy although the government a few years back claimed a stake in the lucrative business.
Marijuana, a drug derived from the leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds of either the Cannabis sativa or Cannabis indica plant contains a chemical called tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) that has mind-altering properties when used appropriately.
A recent study has revealed that despite it being less addictive and a very lucrative plant, Marijuana has continuously proved crucial health-wise with scientists saying it reduces chemotherapy-induced vomiting and nausea for people going through cancer treatment. It can also help to reduce nerve damage pain (neuropathy) in people with HIV or other conditions.
According to the study conducted in 2007, experts revealed that a couple of drugs very addictive than cannabis, and these were given a mean dependence score. This dependence score was based on the perceived risks of intense pleasure, physical dependence, and psychological dependence. Let’s take a look at some of the addictive drugs ranked highest.
1. Heroin: Heroin is a substance that has a reputation for being incredibly addictive. The reasons for its addictive nature have to do with how it works on the mind and the body. When heroin is introduced into the body, it binds with opioid receptors in the mind to stimulate pleasure by releasing dopamine a way beyond what the body can produce on its own.
Unfortunately, once heroin is removed from the system, the body won’t produce dopamine for a period of time. This will cause a variety of symptoms, including depression, nausea, physical pain, and hallucinations. To avoid these symptoms, people may continue to use heroin.
2. Crack Cocaine: Just slightly under heroin sits crack cocaine, a type of cocaine that is smoked, rather than snorted. Crack cocaine is chemically very similar to normal cocaine, but it takes effect more quickly and, due to its potent nature, creates a more intense high. This high decreases in about 10 minutes, which is quicker than powder cocaine’s 30 minutes., a result, increasingly higher doses are often necessary.
Those who use crack cocaine experience a high that creates feelings of high energy, happiness, and excitement. These feelings are more extreme than naturally occurring instances, and as crack wears off, it causes increased depression, anger, and anxiety. Though the withdrawal effects of crack cocaine are short-lived, they are extreme, and fending them off requires often increasingly higher doses. As a result, nearly half a million people in the country are currently addicted to crack cocaine.
3. Nicotine: The finding that nicotine was more addictive than crystal meth and just as addictive as crack cocaine, was a major influence on Nutt being fired. However, studies have shown that nicotine stimulates the activity of a neurotransmitter in the brain, named nicotinic, and makes it necessary to ingest nicotine regularly.
As a result, withdrawal symptoms (such as anxiety, mood swings, and headaches) are common when people try to quit smoking or chewing tobacco. These symptoms are often .ry severe, and easy access to nicotine products makes it easier to relapse than with many other substances. As a result, it is estimated that one in every five deaths in the country was influenced by nicotine use.
4. Methadone
The use of methadone in opiate withdrawal cases has been common for decades because it is a healthier and cleaner alternative. Like heroin, it is an opiate, albeit one that is less addictive. In a medical setting, methadone doses are carefully monitored and tapered to decrease withdrawal symptoms and to decrease the risk of developing an addiction. Unfortunately, addiction is All possible.
5. Crystal Meth: Crystal meth is an alternative form, methamphetamine that does something that its parent drug does not: teach your brain to crave it. When someone smokes crystal meth, they are stimulating the areas, the brain that produce dopamine and norepinephrine, the chemical that increases your feeling of alertness. As a result, those who use crystal mA f feel increased energy and a more “focused state that helps them perform a task more efficiently.
Unfortunately, the brain can become reliant on these artificially increased doses of dopamine and norepinephrine. However, crystal meth also damages the neurons that produce these chemicals and makes them less effective at producing them. As a result, those who suffer from crystal meth addiction may have a permanently decreased ability to feel pleasure and focus.
If you would like your article/opinion to be published on Uganda’s most authoritative news platform, send your submission on: [email protected]. You can also follow DailyExpress on WhatsApp and on Twitter (X) for realtime updates.



