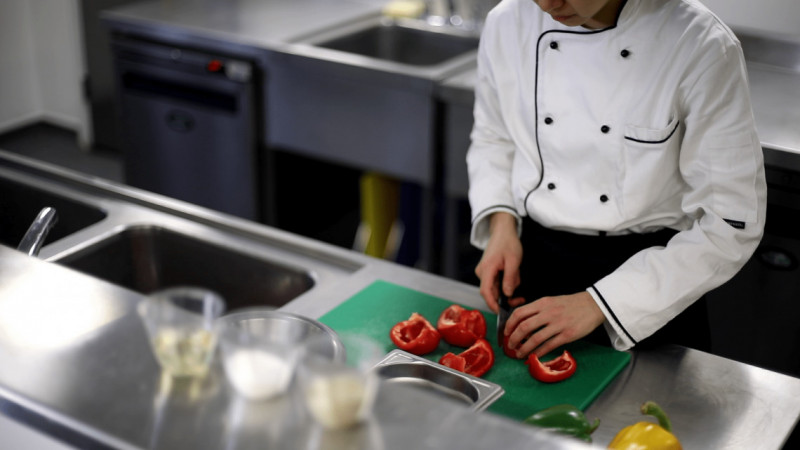
In 2006, World Health Organization shows that globally, food-borne diseases remain responsible for high levels of morbidity and mortality in the general population, but particularly for at-risk groups, such as infants and young, children, the elderly and the immunocompromised. Each day millions of people become ill and thousands die from food-borne diseases.
In order to reduce the incidence and economic consequences of foodborne diseases, the WHO Department of Food Safety, Zoonoses and Foodborne Diseases (FOS) has been assisting the Member States to establish and strengthen their programmes for assuring the safety of food from production to final consumption. WHO produces and disseminates materials for educating consumers about the risks present in food and the safe food handling behaviors that can help minimize those risks.
Food hygiene are all measures needed to ensure the safety and suitability of food at all stages of the food chain which includes production, transportation, storage, marketing, preparation, serving, and consumption to avoid damage and contamination. Poor food hygiene affects the safety of food and thus contaminating it with microbes such as bacteria, protozoa, heavy metals etc. Food-borne illnesses are recognized to be a significant public health problem in Uganda, though data are lacking that would permit curate quantification of morbidity and mortality.
World health organization recommends the following ways we keep food hygiene and prevent the foodborne illness burden:
Keep clean: this involves hand washing before handling food and often during food preparation, after going to the toilet. Cover the wounds or cuts on hands or arms properly with water proof plasters to avoid contact with food. Protect kitchen areas and food from pests and insects
Separate raw food and ready to eat food: This involves storing ready to eat food at upper apartments to prevent it from being contaminated by the dripping of raw food. Use separate knives and cutting board for raw foods and ready to eat food. Always cover the food to avoid cross contaminations.
Cook food thoroughly: Cook food thoroughly especially meat, poultry, eggs and sea food, Re-heat left over food to 75 deg c or above before consumption and Consume cooked food within two hours
Keep food at safe temperatures: Do not leave food at room temps for more than 2 hours and Keep cold dishes and perishable foods in refrigeration at below 4 deg c. Keep hot foods in heating containers above 60 deg c prior to serving.
Use safe water and raw materials: Buy raw materials from reputable shops. Select fresh and wholesome foods. Use portable water to clean raw materials. Wash raw fruits and vegetables thoroughly, especially if eaten raw. Do not use food beyond its expiry.
If the above WHO strategies are implemented, we shall ensure that the food we consume is safe and is of the right quality thus reducing on the foodborne diseases.
If you would like your article/opinion to be published on Uganda’s most authoritative news platform, send your submission on: [email protected]. You can also follow DailyExpress on WhatsApp and on Twitter (X) for realtime updates.



